Understanding the source of high electricity bills can be challenging, particularly when hot water usage plays a significant role. Hot water systems, though essential, can contribute considerably to energy costs if not managed efficiently.
In this article, we'll explore why your hot water system might be causing a spike in electricity bills, common inefficiencies, and actionable steps to minimize energy usage and save on costs.
Understanding Your Hot Water System
Overview of Hot Water Systems
Hot water systems vary in type and function, each with unique energy requirements. The most common types include:
- Electric Water Heaters: Electric Water Heater systems use electrical resistance elements to heat water, often requiring a considerable amount of energy, especially if they are older or have a large storage capacity.
- Gas Water Heaters: Powered by natural gas or propane, these systems can be more energy-efficient than electric heaters but may still have their own inefficiencies.
- Heat Pumps: Operating on the principle of extracting heat from the air, heat pumps are among the most energy-efficient options, although they may incur higher initial costs.
- Solar Water Heaters: These systems use solar panels to capture and convert sunlight into energy for heating water, which can significantly reduce electricity usage if installed and maintained properly.
How Much Electricity Does a Hot Water System Use?
The total number of electricity your hot water system consumes based on the type of system. Electric water heaters generally use between 2 - 4 kWh daily, while heat pump water heaters are significantly more energy-efficient, typically consuming only 1 to 2 kWh per day.
This is why heat pumps one of the most affordable, cost-effective and environmentally friendly choices.
Although gas heaters don't require much electricity for heating, they do need some for ignition and controls. the overall electricity usage will depend on the efficiency of your system and your hot water consumption.
Importance of Energy Management
Effectively managing your hot water system can prevent unnecessary energy consumption and cut down on utility costs. This involves routine checks on system functionality and understanding the system's energy demands in your specific household setup.
1. Breakdown of Hot Water Energy Usage
Heating water can account for a substantial percentage of your home's total electricity usage. Factors affecting hot water energy use include the number of people in the household, frequency of hot water use (e.g., for showers, laundry, and dishwashing), and the type of hot water system installed.
Inefficient or outdated systems require more electricity to maintain adequate hot water supply, resulting in higher bills.
2. Common Causes of High Electricity Usage from Hot Water Systems
Several issues can lead to excess electricity usage in hot water systems:
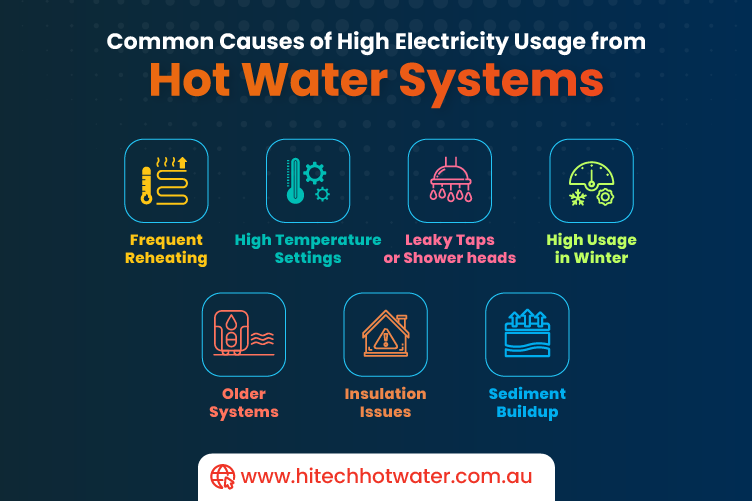
- Older Systems: Older electric heaters or even some outdated gas heaters tend to be less energy-efficient and may struggle to maintain a steady temperature, requiring constant heating and additional energy.
- Frequent Reheating: Storage water heaters continuously reheat the water in their tanks, consuming significant electricity.
- High Temperature Settings: Setting the water temperature too high not only consumes more energy but also risks scalding. Ideally, water heaters should be set at around 50°C (122°F) for optimal energy use.
3. Insulation Issues and Energy Loss
A lack of insulation around hot water pipes and tanks can result in substantial energy loss as heat dissipates into the surrounding environment.
When heat escapes, the system needs to work harder to maintain the desired temperature, leading to higher energy consumption. Adding insulation to both the tank and pipes can significantly reduce this problem.
4. Identifying Other Potential Causes
Apart from system-related inefficiencies, there are other factors that can lead to high energy use for hot water:
- Leaky Taps or Showerheads: Even small leaks can waste a lot of hot water over time, forcing the heater to work more frequently.
- Sediment Buildup: In areas with hard water, minerals like calcium and magnesium accumulate at the bottom of the tank, insulating the heating element and making it harder to heat water effectively.
- High Usage in Winter: Cold weather leads to colder water entering the system, which means the heater needs to work harder to reach and maintain the desired temperature.
5. Practical Tips for Reducing Hot Water Energy Usage
To make your hot water system more energy-efficient and reduce electricity bills, consider these practical tips:

- Lower the Thermostat Setting: Reduce the temperature setting to a moderate level. For most homes, 50°C (122°F) is sufficient.
- Use Insulation: Insulate your hot water tank and pipes to retain heat for longer periods.
- Fix Leaks: Repair any dripping taps or leaking showerheads to prevent water and energy wastage.
- Upgrade Showerheads: Install low-flow showerheads that use less water but still offer a strong flow, thus reducing the amount of hot water needed.
- Limit Hot Water Usage: Use cold water for laundry and other household tasks that don't necessarily require hot water.
1. When to Consider Upgrading Your System
If your electricity bills continue to rise despite taking preventative measures, it might be time to consider upgrading your hot water system. Here's when an upgrade might be warranted:
Signs It's Time to Upgrade
- Frequent Repairs: If your system requires frequent repairs, upgrading may be more cost-effective in the long run.
- Age of System: Hot water systems over 10–15 years old are typically less efficient and may no longer meet modern energy efficiency standards.
- Inconsistent Water Temperature: Difficulty maintaining a consistent hot water supply may indicate an outdated or failing system.
Benefits of Modern Hot Water System Solutions
Upgrading to a new heat pump water heaters or another energy-efficient system can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Lower Operating Costs: Modern systems use less energy, translating into reduced electricity bills.
- Eco-Friendly: Systems like heat pumps have lower carbon footprints, making them a more sustainable option.
- Reliability: Newer models are designed to meet today's high energy efficiency standards, ensuring a steady hot water supply without excessive energy use.

Conclusion
Understanding the factors behind high electricity usage from your hot water system can help you identify ways to save energy and reduce costs.
Whether it's addressing insulation issues, replacing an outdated system, or simply adjusting usage habits, there are several ways to tackle the challenge of high bills.
If you're experiencing consistently high electricity costs, consider evaluating your system and investing in a more efficient solution like a heat pump water heater.
Not only can this reduce your household's environmental impact, but it can also qualify you for valuable heat pump hot water rebates, making the transition even more affordable.






