Inflation in Australia has reached a 30-year high, driving up the costs of everyday essentials, including energy and utility expenses. Since 2020, prices have risen by an average of 22%, with gas and electricity costs escalating significantly.
For homeowners, this translates to higher operational expenses for hot water systems. These trends make it vital to adopt energy-efficient solutions like hot water heat pumps to combat rising costs and ensure long-term savings.
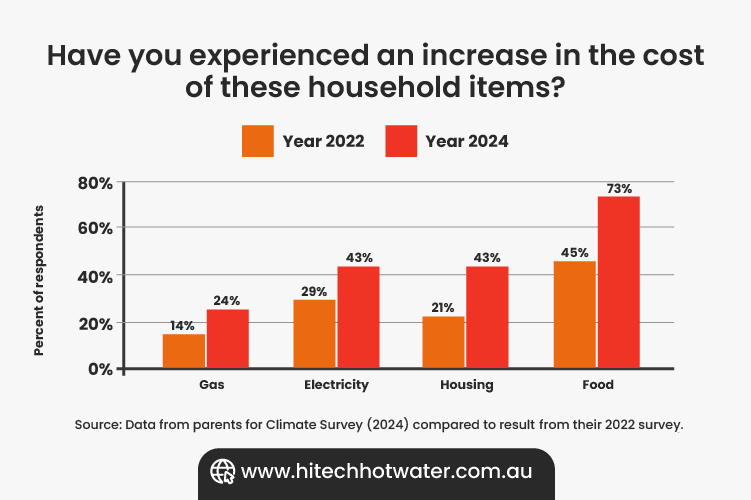
Image Source: Under Pressure Climate Council Report
Rising Inflation and Its Impact on Utilities
According to the Climate Council Report, inflation has driven the cost of household utilities, particularly gas and electricity, to unprecedented levels. Since 2020, gas prices have surged by up to $750 annually for Australian households, directly impacting water heating costs.
Rising energy bills are further compounded by the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, which strain infrastructure and raise utility prices.
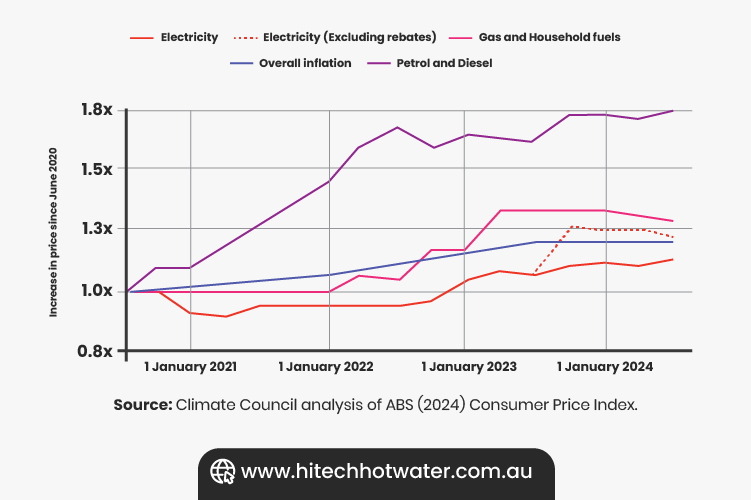
Image Source: Under Pressure Climate Council Report
The transition from traditional gas-powered water systems to electric systems, such as heat pumps, is becoming a key strategy for reducing household energy bills. However, inflation has also influenced the costs of these systems, pushing homeowners to make smarter choices sooner rather than later.
Historical Context: Climate Events and Inflation
Historically, inflation in Australia has been exacerbated by climate-driven events like floods and heatwaves, which increase insurance premiums and household costs. As noted in reports by Sustainability Victoria, gas systems are becoming increasingly cost-prohibitive, especially as utility prices fluctuate.
This reinforces the need for alternatives like heat pump systems, which use renewable energy sources and operate more efficiently during off-peak electricity hours.
An infographic from the Climate Council illustrates the steady rise in inflation, directly correlating with higher energy costs and an urgent need for energy-efficient solutions.
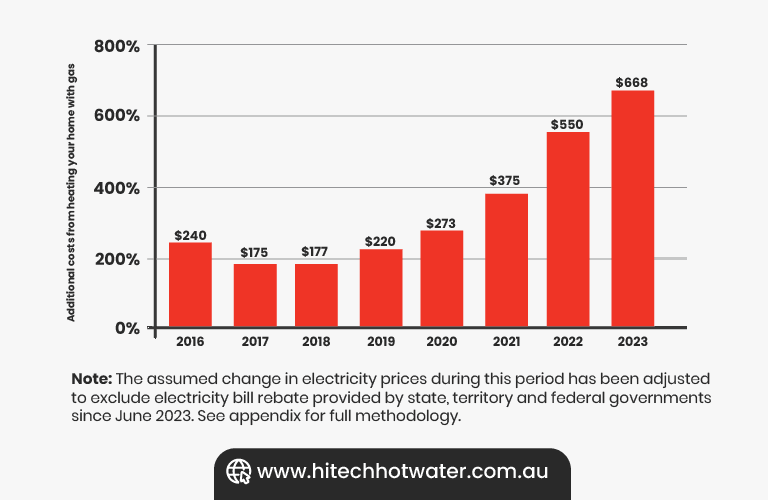
Image Source: Under Pressure Climate Council Report
Decline in Rebates and Incentives
Government rebates for energy-efficient systems, including heat pumps, are gradually declining as federal and state budgets shift focus on broader renewable energy projects.
This trend is documented in a report by the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), which emphasizes the importance of acting quickly to take advantage of current incentives.
Currently, key rebates such as the Small-scale Technology Certificates (STCs) and Victorian Energy Upgrades (VEU) are available in Victoria. In New South Wales (NSW), homeowners can benefit from the Energy Savings Scheme (ESC) along with Small Scale Technology Certificate (STC), both of which provide significant support for energy-efficient upgrades.
Homeowners across Australia are urged to act now. Upgrading to an energy-efficient system, such as hot water heat pumps, ensures long-term financial and environmental benefits while still allowing access to these valuable rebates. Delaying could mean missing out on these incentives as programs evolve or phase out.
Supply Chain Challenges Post-Pandemic
The pandemic has left lasting impacts on supply chains, increasing the costs of manufacturing and shipping hot water systems. Component shortages have driven up prices, and logistical delays mean longer wait times for installations.
This situation is particularly true for advanced systems like heat pumps, which rely on specific parts.
Manufacturers are now shifting their focus toward electric systems to meet growing demand, as homeowners prioritize energy-efficient solutions.
This shift is highlighted by Renew Economy, which describes heat pumps as a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional systems, particularly when paired with solar PV systems.
Electricity vs. Gas: Trends in Hot Water Systems
The trend toward energy-efficient hot water systems in Australia is gaining momentum, with many households replacing traditional gas or electric resistance systems with advanced heat pump water heaters.
This shift is driven by both economic and environmental factors. According to Sustainability Victoria, heat pump systems are significantly more cost-effective over the long term, especially when combined with solar PV systems or operated during off-peak hours.
These systems leverage renewable energy to provide consistent hot water while minimizing energy consumption and utility bills.
1.Comparing Operational Costs
Data from the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) underscores the cost advantages of heat pumps compared to traditional gas and electric water heaters.
Heat pumps operate at a fraction of the energy cost, with savings further amplified when paired with solar panels to offset daytime energy use. For instance:
- Gas Water Heaters incur high operational costs due to fluctuating gas prices and inefficient heat transfer.
- Electric Resistance Systems consume substantial electricity, especially during peak tariff hours, leading to elevated energy bills.
- Heat Pumps, in contrast, utilize ambient air and advanced technology to heat water efficiently, providing a reduction in energy usage by up to 70%.
2. Environmental and Economic Benefits
Beyond cost savings, heat pumps align with Australia's commitment to reducing carbon emissions. These systems significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to gas heaters, making them a more sustainable choice.
Additionally, their ability to integrate with renewable energy solutions like rooftop solar PV systems positions heat pumps as a cornerstone in Australia's transition to clean energy.
3. Why Heat Pumps are the Future
As the cost of energy continues to rise, homeowners are prioritizing investments in systems that offer both financial and environmental benefits.
Heat pump water heaters not only lower operational costs but also future-proof homes against the volatility of gas and electricity markets.
Their adaptability to modern energy systems and eligibility for government rebates make them an attractive choice for households looking to optimize energy use and minimize expenses.
For homeowners seeking long-term savings and sustainability, heat pumps stand out as the most economical and environmentally friendly solution for hot water systems in the Australian market.
Why Now Is the Right Time to Upgrade

1. Combat Rising Energy Costs:
Upgrading to an energy-efficient heat pump hot water system is one of the most effective ways to reduce utility bills. These systems consume up to 70% less energy than traditional options, providing immediate relief from inflation-driven costs.
2. Take Advantage of Existing Rebates:
Programs like ESC, PERCS, STCs and VEU rebates significantly reduce the upfront cost of heat pumps. Acting now ensures you benefit from these incentives before they decline further.
3. Future-Proof Your Home:
Heat pumps align with Australia's transition to renewable energy, making them a sustainable and environmentally friendly choice. By investing in a heat pump now, homeowners can secure long-term savings and reduce their carbon footprint.
4. Overcome Supply Chain Delays:
While supply chain issues persist, acting quickly minimizes the risk of further delays and price hikes. Securing a heat pump now ensures timely installation and avoids potential shortages.
Government Support for Energy-Efficient Systems
The Australian government has been actively promoting energy-efficient technologies to combat rising energy costs and carbon emissions. Through initiatives like Victorian Energy Upgrades (VEU) program, households can access rebates and incentives for upgrading heat pump water heaters.
These programs aim to reduce the financial burden of switching to efficient systems, making heat pumps an even more attractive option.
According to the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), heat pumps can play a pivotal role in lowering household energy consumption while contributing to national emission reduction targets.
Despite the availability of incentives, recent reports from IEEFA and Climate Council indicate that these programs are evolving, with some rebates seeing reductions as policy shifts focus on broader renewable energy integration.
For households, this signals a pressing opportunity to take advantage of existing incentives before they decrease further.
In New South Wales (NSW), additional programs like the Energy Savings Certificate (ESC) and the Peak Electricity Reduction Certificates Scheme (PERCS) offer further support for energy-efficient upgrades.
These initiatives reward households that adopt technologies like heat pumps by providing financial incentives tied to energy savings and reduced peak electricity demand.
This makes NSW one of the most supportive states for transitioning to efficient water heating systems, alongside Victoria's robust VEU program. Acting now allows homeowners to leverage these diverse rebate opportunities for maximum financial benefit.
The Role of STC Rebates Amid Rising Inflation
Amid rising inflation and increasing energy costs, the Small-scale Technology Certificates (STC) rebate offers Australian homeowners a financial cushion when upgrading to energy-efficient hot water systems like heat pumps.
The STC rebate, part of the federal Renewable Energy Target, reduces the upfront cost of eligible systems based on their energy savings and environmental benefits.
As inflation drives up the cost of goods and services, this rebate becomes even more valuable, offsetting a significant portion of the installation expense.
However, with inflation affecting government budgets and rebate programs evolving, homeowners are encouraged to act quickly to secure these incentives before potential reductions.
By leveraging the STC rebate, Australians can mitigate the financial burden of transitioning to a more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable hot water solution.
Long-Term Economic Benefits
Data from Sustainability Victoria confirms that households transitioning to heat pump water heaters can save hundreds of dollars annually compared to gas and electric resistance systems.
A heat pump paired with a solar PV system can nearly eliminate operational costs, especially when used during off-peak hours.
Additionally, the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES) administered by the federal government provides Small-scale Technology Certificates (STCs), which further offset the upfront cost of heat pump installations.
These programs are designed to encourage early adoption of efficient technologies, helping homeowners mitigate the impact of rising energy prices. The sooner households switch to heat pumps, the more they can benefit from these financial incentives and long-term cost reductions.
Environmental Impact and Government Goals
The Australian government has set ambitious targets to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, and heat pumps are integral to this plan.
According to ARENA, water heating contributes significantly to household energy use and carbon emissions. By replacing gas-based systems with heat pumps, households can reduce their environmental footprint by up to 70%, aligning with the national sustainability goals.
Moreover, the Climate Council Report highlights that the transition to energy-efficient systems like heat pumps supports Australia's efforts to minimize dependency on fossil fuels. Heat pumps utilize renewable resources and modern technology, ensuring that households contribute to a cleaner, greener future.
A Resilient Solution in the Face of Supply Chain Disruptions
The global supply chain disruptions triggered by the pandemic highlighted the vulnerability of traditional energy systems reliant on imported gas and outdated electric water heaters. Heat pumps, which use localized and renewable energy sources, offer a resilient alternative.
According to Renew Economy, the shift towards heat pumps aligns with the broader movement towards decentralized energy systems, reducing dependence on fluctuating global energy markets.
Households that invest in heat pumps not only mitigate the impact of inflation but also gain a long-term solution that is less susceptible to geopolitical or economic disruptions.
Supporting Energy Independence with Heat Pumps
The Australian government's push for energy independence through renewable technologies further underscores the importance of adopting heat pumps.
Reports from ARENA suggest that heat pumps, when paired with solar PV systems, are critical for reducing household reliance on grid electricity, especially during peak demand.
By using a heat pump with a solar system, households can create a self-sustaining energy loop, generating and storing energy for their hot water needs.
This reduces dependency on external energy suppliers, shielding households from unpredictable energy price hikes.

Conclusion
Rising inflation and energy costs are reshaping the way Australian households approach hot water systems. As utility bills climb, the hot water anode rod plays an increasingly critical role in maintaining system efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Upgrading to a heat pump hot water system not only combats inflation but also aligns with Australia's broader energy transition goals.
With government rebates still available and supply chain issues beginning to stabilize, now is the ideal time to make the switch.
Homeowners are encouraged to explore energy-efficient options and secure their systems before costs rise further. Take advantage of incentives today to enjoy financial savings and environmental benefits for years to come.






